ISIS and Assad cooperate locally on mutual interests to destroy FSA
A source close to the Turkish National Intelligence Organization claims an agreement was made between the Assad regime and ISIS to destroy the Free Syrian Army in the country's north, continue oil sales, assassinate Zahran Alloush and surrender Tedmur and Sukhna
A group of Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham (ISIS) and Syrian regime
commanders held a meeting at a gas production plant in Hasaka's
al-Shaddadi area on May 28 this year. The two warring factions met not
to stop fighting each other, but to focus on a common enemy. The common
enemy to be destroyed was the rebel forces, especially the moderate and
Western-backed Free Syrian Army (FSA), which recently made significant
gains against the regime in Idlib, Aleppo and Deraa. A source close to
the National Intelligence Organization (MİT), speaking on the condition
of anonymity, told Daily Sabah that President Bashar Assad's Syrian
regime and ISIS made an agreement on that day at the gas production
plant.
It has long been claimed that ISIS works for Iran or Assad, but there was no evidence to prove these conspiracy theories. However, when looking at the war conditions, local and temporary agreements are possible. Both Assad and ISIS hate other rebel forces – the regime considers the rebels to be terrorists and has entered a deadly war with them. ISIS sees the rebels as the main obstacle in its path to creating a new state in Iraq and Syria based on a strict interpretation of religious jurisprudence.
It has long been claimed that ISIS works for Iran or Assad, but there was no evidence to prove these conspiracy theories. However, when looking at the war conditions, local and temporary agreements are possible. Both Assad and ISIS hate other rebel forces – the regime considers the rebels to be terrorists and has entered a deadly war with them. ISIS sees the rebels as the main obstacle in its path to creating a new state in Iraq and Syria based on a strict interpretation of religious jurisprudence.
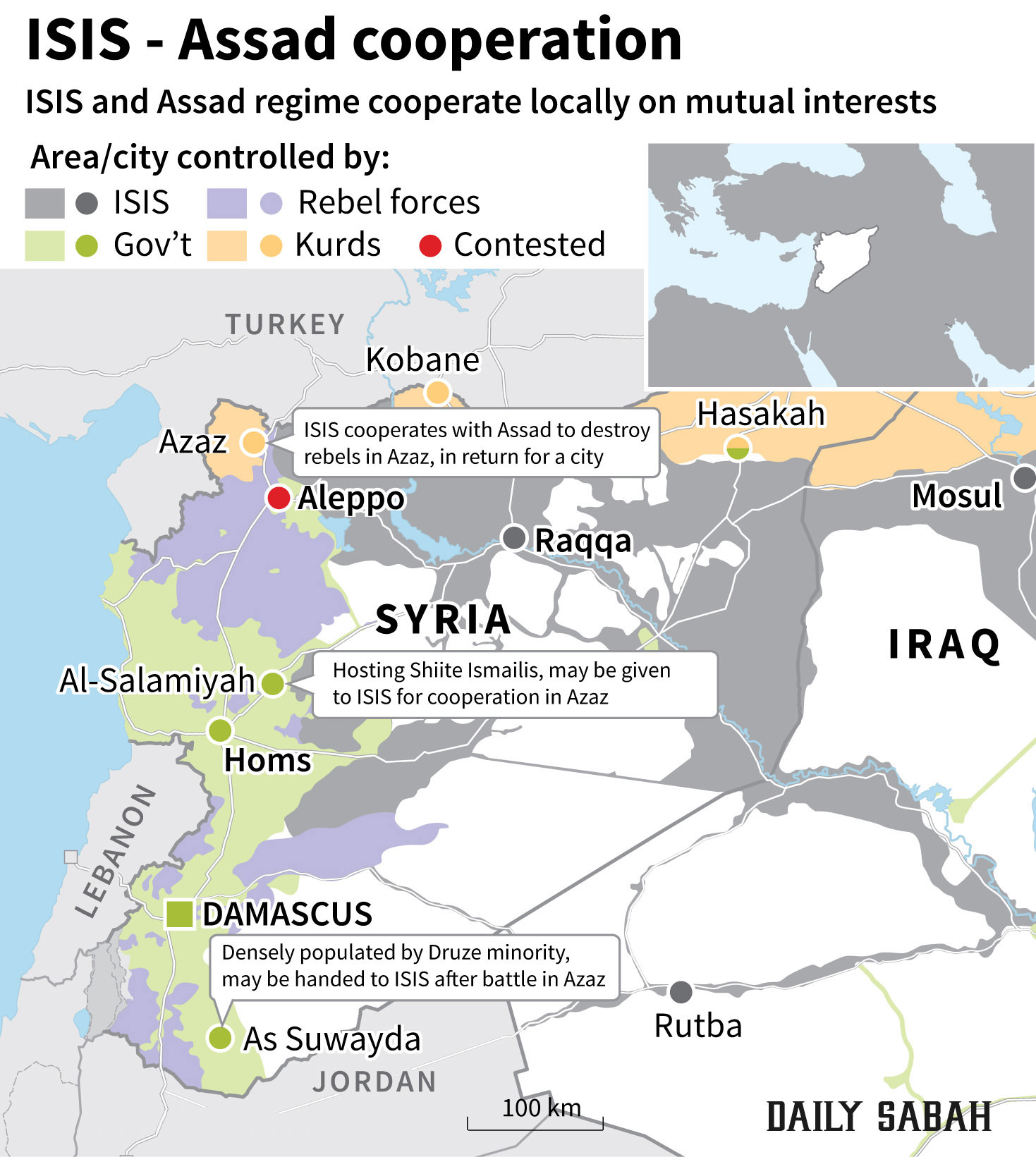
The source revealed that according to the deal, the Assad regime and
ISIS will cooperate in certain areas, especially where they are in
trouble with rebel forces like northern Aleppo, and while ISIS will
increase its attacks on the FSA, the regime will also intensify
airstrikes. Moreover, the Syrian regime asked ISIS to specifically
target some rebel leaders like Zahran Alloush, who controls the Jaysh
al-Islam (Army of Islam) group that operates in east Ghouta in the
Damascus suburbs. As a gift for ISIS' help to the regime against the
FSA, the regime would give some cities like Tedmur and Sukhna to the
militant group. ISIS, in response to the regime's cooperation, will
continue selling oil via both pipelines and tankers. As understood from
the recent developments, there was a dispute between the two parties
over the Kurdish areas. Regime representatives, according to the source,
rejected the ISIS seizure of Kurdish areas since the regime and the
Kurdish Democratic Union Party's (PYD) People's Protection Units (YPG)
allegedly made a deal previously, ensuring that the Kurdish side and
Damascus will not fight each other and that regime forces will leave the
control of the Kurdish areas to the PYD.
The source told Daily Sabah that the regime and ISIS made an agreement consisting of four articles. The parties would deal with regard to six articles, but one of the last two remained ambiguous, and it was decided they would be discussed later, while the other one remained unsolved. The existence of both cooperation and disputes show that the agreement is temporary and focuses on the common enemy.
According to the source, two officials from the regime attended the
meeting – Talal Ali and Colonel Ahmed Abdel Wahhab, who is serving as
head of military intelligence in Qamishli. The envoy arranged the
meeting after Ali Mamlouk, head of the Syrian National Security Bureau,
tasked them with convincing ISIS to increase attacks on the FSA. Mamlouk
had been accused of spying for rebel groups and allying with some other
groups. Yet, according to the information obtained, Mamlouk organizes
meetings for local cooperation with different groups against others.
ISIS sent three commanders about whom Daily Sabah does not have any
information other than their names – Faisal Ghanem Abu Muhammad, Abu
Ramzy and lawyer Fadel el-Saleem Abu Mustafa – which are most likely
pseudonyms as ISIS members never give more information about themselves.
Even members of the group have limited information on governors and
commanders.
The two parties agreed on four issues:
1) Sukhna and Tadmur will surrender to ISIS with weapons in warehouses
Tadmur or Palmyra and Sukhna are strategically important for ISIS to consolidate its power in Syria by capturing cities that are in the middle of the country and at the interception point of oil and gas pipelines. Syrian forces loyal to Assad that have lost power in the north and around Palmyra were unable to control the area, as the FSA and other rebel forces were attempting to capture it. ISIS was also aiming to capture the area and did so without facing any serious struggle from regime forces. After taking Palmyra, ISIS destroyed the border between Syria and Iraq. A week before the meeting, ISIS militants were seizing control of villages in rural areas. On May 22, Al-Arabiya News reported that ISIS militants took control of the Syrian side of the al-Waleed border crossing that connects Syria with Iraq. As a result, Syrian forces were trapped and chose not to fight. While pulling back, the regime left an army intelligence outpost and a military airport. Apart from Tadmur, another strategically important city was Sukhna. On March 18 syriadirect.org reported: "The regime considers Sukhna the last line of defense between ISIS forces invading from the town's north and regime-controlled Palmyra to the town's south. A victory for ISIS would give it access to some of the richest oil and gas fields in the country – a crucial gain for the militant group as the country suffers from an acute fuel crisis and as the U.S.-led coalition continues to target its oil production facilities in Deir ez-Zor, al-Hasakah and Raqqah." The regime, which is in trouble with the advance of rebels both in Damascus's north, Idlib and Deraa, agreed to give the two cities to ISIS. But the regime's demand was clear in the second article.
1) Sukhna and Tadmur will surrender to ISIS with weapons in warehouses
Tadmur or Palmyra and Sukhna are strategically important for ISIS to consolidate its power in Syria by capturing cities that are in the middle of the country and at the interception point of oil and gas pipelines. Syrian forces loyal to Assad that have lost power in the north and around Palmyra were unable to control the area, as the FSA and other rebel forces were attempting to capture it. ISIS was also aiming to capture the area and did so without facing any serious struggle from regime forces. After taking Palmyra, ISIS destroyed the border between Syria and Iraq. A week before the meeting, ISIS militants were seizing control of villages in rural areas. On May 22, Al-Arabiya News reported that ISIS militants took control of the Syrian side of the al-Waleed border crossing that connects Syria with Iraq. As a result, Syrian forces were trapped and chose not to fight. While pulling back, the regime left an army intelligence outpost and a military airport. Apart from Tadmur, another strategically important city was Sukhna. On March 18 syriadirect.org reported: "The regime considers Sukhna the last line of defense between ISIS forces invading from the town's north and regime-controlled Palmyra to the town's south. A victory for ISIS would give it access to some of the richest oil and gas fields in the country – a crucial gain for the militant group as the country suffers from an acute fuel crisis and as the U.S.-led coalition continues to target its oil production facilities in Deir ez-Zor, al-Hasakah and Raqqah." The regime, which is in trouble with the advance of rebels both in Damascus's north, Idlib and Deraa, agreed to give the two cities to ISIS. But the regime's demand was clear in the second article.
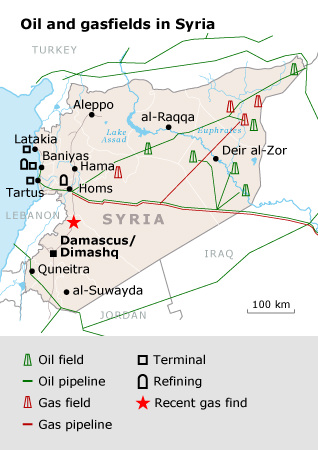
2) ISIS will continue selling oil to the regime via both pipelines and tankers
According to the deal, ISIS will not cut off the regime's access to energy and will continue selling oil through the pipelines that go into regime-held areas as well as through tankers that will take the oil to where pipelines have been destroyed or heavily damaged. Palmyra is also important for its gas resources.
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights said last month that ISIS controls half of all the territory in the war-torn country. The map clearly shows almost all major oil fields are controlled by ISIS, which also controls a vast oil-rich area in Iraq. By seizing Palmyra and unifying its borders from Mosul to Palmyra, ISIS started holding the two countries' major oil resources. The Assad regime has been deprived of almost half of its gas and electricity resources after ISIS's advances.
ISIS was aware of the importance of the natural resources and that the resources would give it greater power than that which it could gain through fighting. Assad would have to cooperate with ISIS as the group is holding major oil and gas fields. Touching on the importance of Palmyra, Yezid Sayigh, in an article published by the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace on June 8, wrote: "Fields in the area [of Palmyra] were expected to eventually produce 9 million cubic meters of crude oil per day. These included the Arak, Dubayat, Hail, Hayan, Jihar, al-Mahr, Najib, Sukhneh and Abi Rabah fields, which according to a former industry insider have collectively been producing half of Syria's output of natural raw and liquid petroleum gas. Palmyra is also the transit point for pipelines carrying gas from important fields in Hasakah and Deir ez-Zor provinces in northeastern and eastern Syria respectively."
According to the deal, ISIS will not cut off the regime's access to energy and will continue selling oil through the pipelines that go into regime-held areas as well as through tankers that will take the oil to where pipelines have been destroyed or heavily damaged. Palmyra is also important for its gas resources.
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights said last month that ISIS controls half of all the territory in the war-torn country. The map clearly shows almost all major oil fields are controlled by ISIS, which also controls a vast oil-rich area in Iraq. By seizing Palmyra and unifying its borders from Mosul to Palmyra, ISIS started holding the two countries' major oil resources. The Assad regime has been deprived of almost half of its gas and electricity resources after ISIS's advances.
ISIS was aware of the importance of the natural resources and that the resources would give it greater power than that which it could gain through fighting. Assad would have to cooperate with ISIS as the group is holding major oil and gas fields. Touching on the importance of Palmyra, Yezid Sayigh, in an article published by the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace on June 8, wrote: "Fields in the area [of Palmyra] were expected to eventually produce 9 million cubic meters of crude oil per day. These included the Arak, Dubayat, Hail, Hayan, Jihar, al-Mahr, Najib, Sukhneh and Abi Rabah fields, which according to a former industry insider have collectively been producing half of Syria's output of natural raw and liquid petroleum gas. Palmyra is also the transit point for pipelines carrying gas from important fields in Hasakah and Deir ez-Zor provinces in northeastern and eastern Syria respectively."
3) ISIS will attack rebel-held areas and Assad's forces will carry out airstrikes
According to the agreement, ISIS will attack rebel-held areas in northern Aleppo, especially in Azaz, and the regime will intensify its airstrikes.
According to the agreement, ISIS will attack rebel-held areas in northern Aleppo, especially in Azaz, and the regime will intensify its airstrikes.
After ISIS was defeated by Kurdish forces in Tal Abyad, the group
targeted FSA-held Azaz, a strategically important town near the Turkish
border. An activist, who wanted his name to be concealed for security
reasons and has close relations with the Ahrar al-Sham group, told Daily
Sabah that regime strikes and ISIS attacks are simultaneous. "When ISIS
militants started terrorizing villages near Azaz and Aleppo's rural
areas, the regime started dropping more barrel bombs. Until two weeks
ago the regime had lessened the airstrikes as the opposition groups were
targeting new areas closer to Latakia and Damascus. When ISIS left Tal
Abyad with little resistance, Assad's airplanes started flying over
Azaz." A source in Syria, who wanted to remain anonymous, highlighted
that ISIS is not fighting against the Assad regime, but only against
opposition groups while also harming civilians caught in the middle. The
same source also claimed that there is a hidden or tacit agreement
between ISIS, the Assad regime and Iran, as the regime and its
supporters benefit from ISIS' commitments. As an example, he said,
"Before ISIS captured Raqqah, the regime was continuously bombing. When
ISIS captured it, there were no more bombings."
Aron Lund, editor of Syria in Crisis, a website published by the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, told Daily Sabah he does not think that there is any form of organized cooperation between Assad and ISIS, but he added that there might be local cooperation. "There may of course exist local arrangements between specific commanders, or for example clan elders on the two sides who know each other, and informal understandings about red lines, given that the situation can be calm for long times on particular fronts." Joshua Landis, director at the Center for Middle East Studies, said that he does not know if Assad and ISIS cooperate in the Aleppo region even as they fight in Palmyra, Homs, Deir ez-Zor and Qalamoun. But he added that any group may cooperate with another other one and did not deny the possibility.
4) If ISIS succeeds in defeating rebels in the north, the regime will give either al-Suwayda or al-Salamiyah to ISIS
Aron Lund, editor of Syria in Crisis, a website published by the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, told Daily Sabah he does not think that there is any form of organized cooperation between Assad and ISIS, but he added that there might be local cooperation. "There may of course exist local arrangements between specific commanders, or for example clan elders on the two sides who know each other, and informal understandings about red lines, given that the situation can be calm for long times on particular fronts." Joshua Landis, director at the Center for Middle East Studies, said that he does not know if Assad and ISIS cooperate in the Aleppo region even as they fight in Palmyra, Homs, Deir ez-Zor and Qalamoun. But he added that any group may cooperate with another other one and did not deny the possibility.
4) If ISIS succeeds in defeating rebels in the north, the regime will give either al-Suwayda or al-Salamiyah to ISIS
According to information obtained by Daily Sabah, the regime promised ISIS that if the rebels were repelled from the north, either al-Suwayda, which is densely populated by the Druze minority, which is considered heretical by ISIS, or al-Salamiyah, which is home to Shiites belonging to the Ismaili sect, would be given to ISIS.
The Fatah Army, a rebel coalition, has won a string of victories in Idlib since early April after ending internal disputes, has been unified and is concentrating on advancing on Latakia. The rebels have recently made the most significant gains since the war started in 2011. They captured Idlib, Jisr al-Shughour, Areha and Deraa.
The two cities offered by the Assad regime would expand ISIS's area of control into Idlib near the Turkish border and Suwayda in the south. In both areas, moderate rebels will have to be beaten first.
The Assad regime, which accuses rebels of persecuting minorities, has allegedly promised to give the two cities to ISIS and pave the way for massacres of both Druze and Ismailis that ISIS considers heathens.
There were two more issues according to the source. One of them will be solved later and another remains disputed.
1) Zahran Alloush will be assassinated
After agreeing on the four articles, the two sides said another meeting will be organized on how to assassinate Zahran Alloush, the head of Jaish al-Islam, which operates in Ghouta and Douma near Damascus and also fights ISIS near the Qalamoun Mountains. The regime, according to the source, asked ISIS to kill Alloush and ISIS accepted the task, but the two groups said they will meet later when ISIS plans how to carry out the assassination.
Jaish al-Islam is known for its successful operations against the regime and Hezbollah near Damascus. In an article published in Foreign Policy on Oct. 1, 2013, the group was described as the winning side after unifying more than 50 small groups under its umbrella. The article claims that the U.S. and Gulf countries, mainly Saudi Arabia, have provided aid to the group based on a report published by The New York Times on March 24, 2013. The article also claims that the U.S. was hoping that the group would stop the rise of extremist groups in Syria. "The formation of the Army of Islam in the capital's eastern fringe under Zahran Alloush, the leader of the group Liwa al-Islam, strengthens Salafist militants owing allegiance to Riyadh against ISIS," a Reuters report said on Oct. 1, 2013. "While hoping to avoid outright confrontation with fellow militants, the Saudis had been gauging the willingness of local Salafist fighters in joining Saudi-backed formations, including a proposed Syrian National Army," the same report said. In sum, Jaish al-Islam was supposed to both stop ISIS and al-Qaida-affiliated groups and disturb the regime. Neither ISIS nor al-Nusra Front is effective in the south.
After agreeing on the four articles, the two sides said another meeting will be organized on how to assassinate Zahran Alloush, the head of Jaish al-Islam, which operates in Ghouta and Douma near Damascus and also fights ISIS near the Qalamoun Mountains. The regime, according to the source, asked ISIS to kill Alloush and ISIS accepted the task, but the two groups said they will meet later when ISIS plans how to carry out the assassination.
Jaish al-Islam is known for its successful operations against the regime and Hezbollah near Damascus. In an article published in Foreign Policy on Oct. 1, 2013, the group was described as the winning side after unifying more than 50 small groups under its umbrella. The article claims that the U.S. and Gulf countries, mainly Saudi Arabia, have provided aid to the group based on a report published by The New York Times on March 24, 2013. The article also claims that the U.S. was hoping that the group would stop the rise of extremist groups in Syria. "The formation of the Army of Islam in the capital's eastern fringe under Zahran Alloush, the leader of the group Liwa al-Islam, strengthens Salafist militants owing allegiance to Riyadh against ISIS," a Reuters report said on Oct. 1, 2013. "While hoping to avoid outright confrontation with fellow militants, the Saudis had been gauging the willingness of local Salafist fighters in joining Saudi-backed formations, including a proposed Syrian National Army," the same report said. In sum, Jaish al-Islam was supposed to both stop ISIS and al-Qaida-affiliated groups and disturb the regime. Neither ISIS nor al-Nusra Front is effective in the south.
2) ISIS wants al-Hasakah, regime refuses
The disputed proposal was the Kurdish region, especially al-Hasakah, which is at the center of a corridor for the Kurdish-populated areas. ISIS wanted to seize al-Hasakah to break the PYD's power in the region to secure the north while attacking the FSA in the north of Aleppo. However, according to the source, regime representatives asked ISIS not to attack the Kurdish area as the regime and the PYD previously agreed that al-Hasakah will remain in the hands of the YPG.
However, ISIS did not accept the regime's demand and attacked al-Hasakah. A clash between the group and the regime erupted near Hama in Sheik Hilal. "The clashes killed 40 government loyalists, including soldiers and members of the National Defense Forces," a local pro-government militia said. The latest clash could show that cooperation is not valid across Syria, but has a specific target to destroy
The disputed proposal was the Kurdish region, especially al-Hasakah, which is at the center of a corridor for the Kurdish-populated areas. ISIS wanted to seize al-Hasakah to break the PYD's power in the region to secure the north while attacking the FSA in the north of Aleppo. However, according to the source, regime representatives asked ISIS not to attack the Kurdish area as the regime and the PYD previously agreed that al-Hasakah will remain in the hands of the YPG.
However, ISIS did not accept the regime's demand and attacked al-Hasakah. A clash between the group and the regime erupted near Hama in Sheik Hilal. "The clashes killed 40 government loyalists, including soldiers and members of the National Defense Forces," a local pro-government militia said. The latest clash could show that cooperation is not valid across Syria, but has a specific target to destroy


هیچ نظری موجود نیست:
ارسال یک نظر